- Treatment
Landscape- ABSSSI
Treatment
Burden- ABSSSI
Treatment
Challenges- About
KIMYRSA®- What is
KIMYRSA®?- Mechanisms
of Action- PK Profile
- In Vitro
Results by Pathogen- Clinical
Studies- Clinical Study Information
- SOLO Studies
- Real-World
Experience- Real-World Studies
- Real Patient Results
- Clinical Expert Videos
- Single-Dose
Administration- Resources
and Support- Patient Support Programs


KIMYRSA®—similar PK profile to ORBACTIV® with a shorter 1-hour infusion1
The PK study of KIMYRSA® bridges to the clinical efficacy and safety of another oritavancin product, ORBACTIV®.
Mean oritavancin concentration (µg/mL) vs time, linear scale (PK population) in patients with ABSSSI1,2a
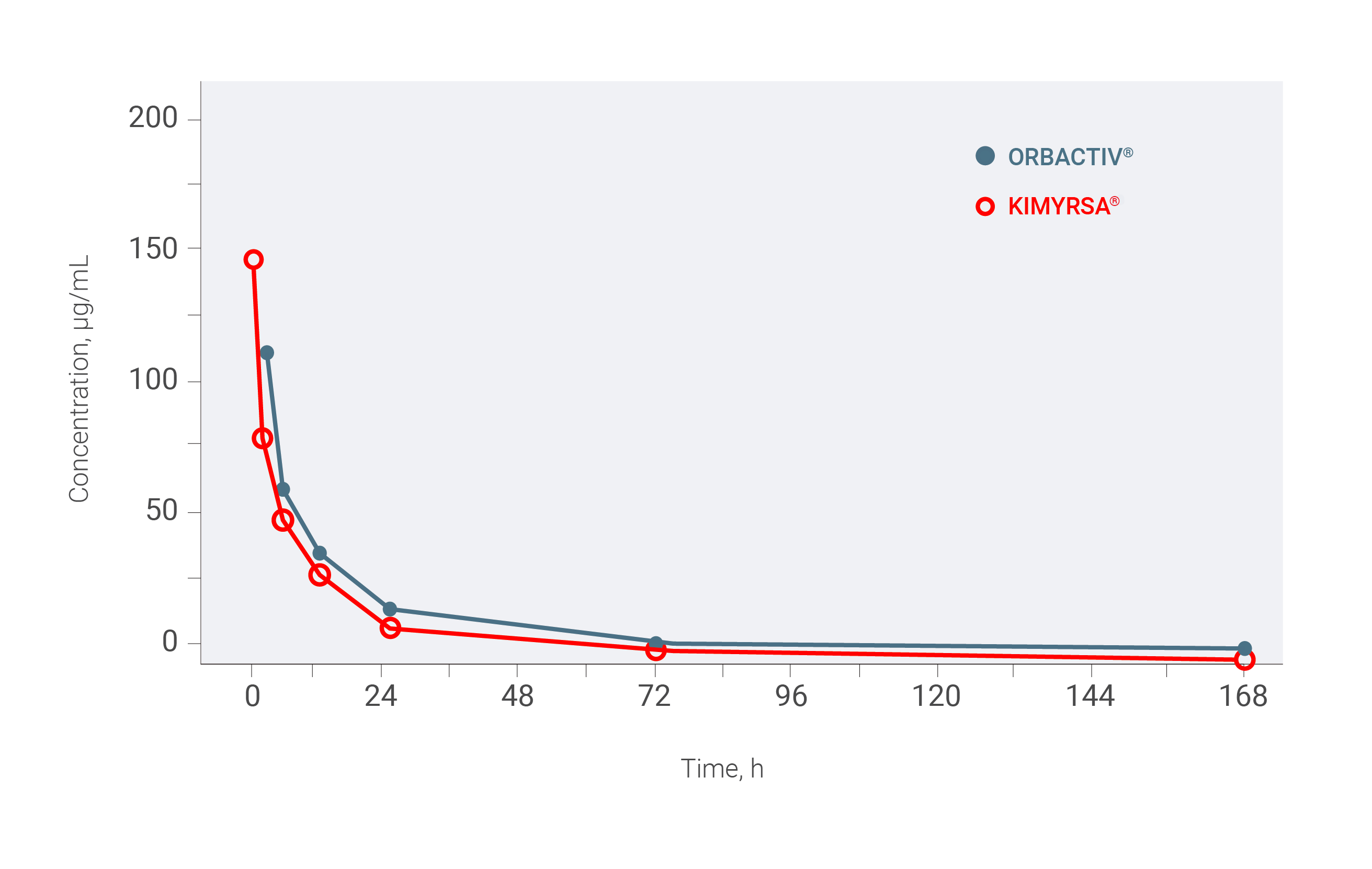
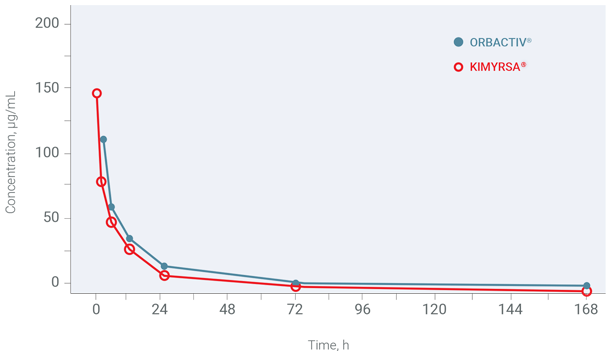
aBased on results from a randomized, open-label, multicenter, pharmacokinetics study that compared KIMYRSA® administered over 1 hour (n=50) to ORBACTIV® administered over 3 hours (n=52) in adult patients with ABSSSI.1
Mean (±SD) PK parameters following a single 1,200-mg dose of KIMYRSA® by IV infusion over 1 hour (N=50) and ORBACTIV® by IV infusion over 3 hours (N=50) in patients with ABSSSI2a

Pharmacokinetic parameter
KIMYRSA®(1 hour)
mean (±SD)ORBACTIV®(3 hour)
mean (±SD)Cmax(µg/mL) 148 (±43.0) 112 (±34.5) AUC0-72(h•µg/mL) 1,460 (±511) 1,470 (±582) AUC0-72, area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time zero to 72 hours; Cmax, maximum plasma concentration; SD, standard deviation.2
Oritavancin demonstrated rapid bactericidal action in vitro8,9a
Bacterial burden over time, oritavancin vs dalbavancin and vancomycin8
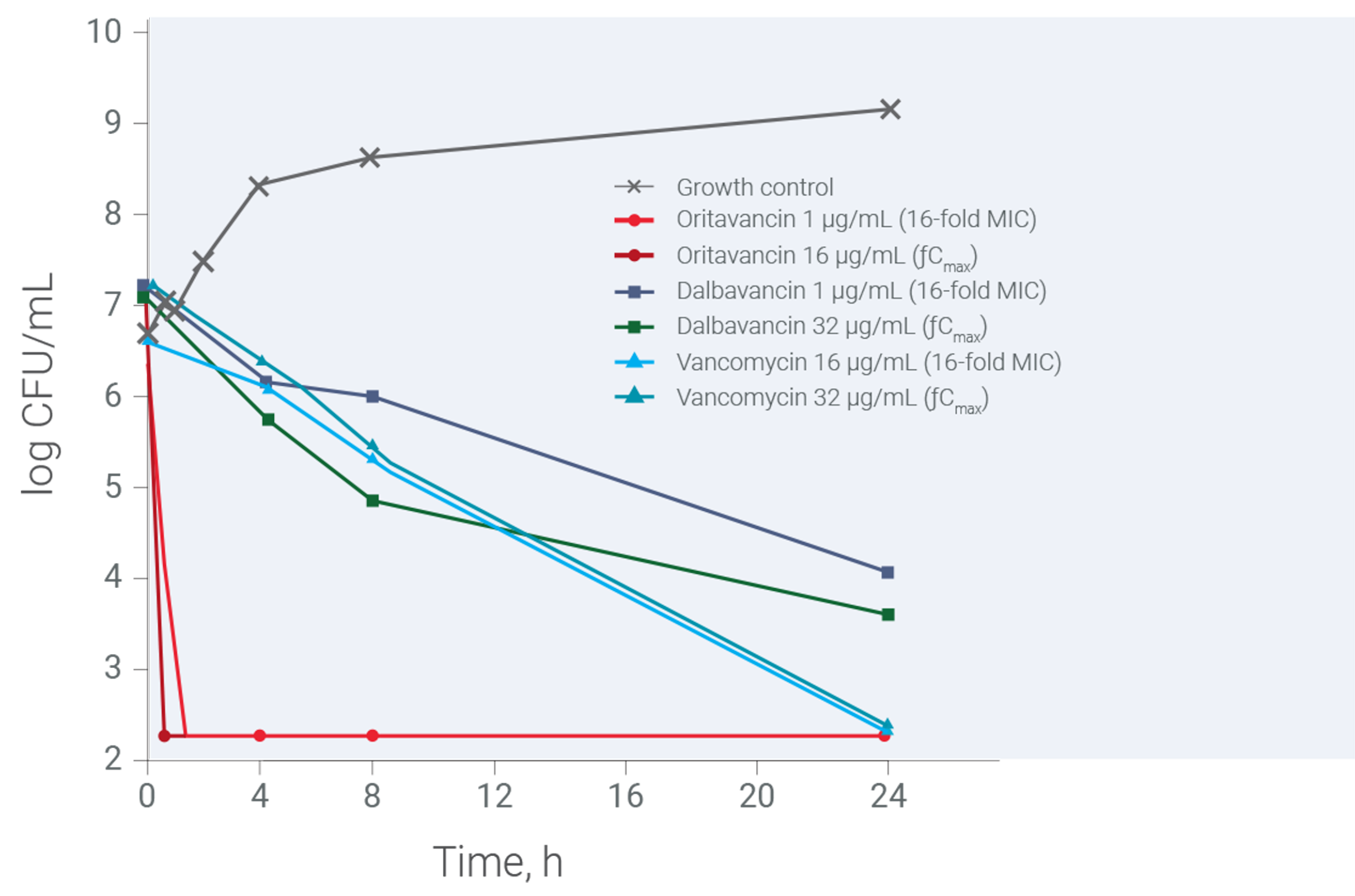
- Killing of MRSA isolate (ATCC 43300) by oritavancin was rapid, with bactericidal activity within 1 hour8†
- In contrast, the bactericidal activities of dalbavancin and vancomycin occurred more slowly over the 24-hour period8†
- The rapid concentration-dependent bactericidal activity of oritavancin results from multiple mechanisms of action. The time-dependent bactericidal activity of dalbavancin results from a single mechanism that is shared with vancomycin8
aORBACTIV® (oritivancin) has head-to-head clinical trial data versus vancomycin only. In vitro activity does not necessarily correlate to clinical efficacy.
† Bactericidal activity defined as a ≥3 log reduction in bacterial viability at 24 hours (or earlier, as indicated), relative to the starting inoculum.20
Change in viable bacteria over time at a high inocolum density9†
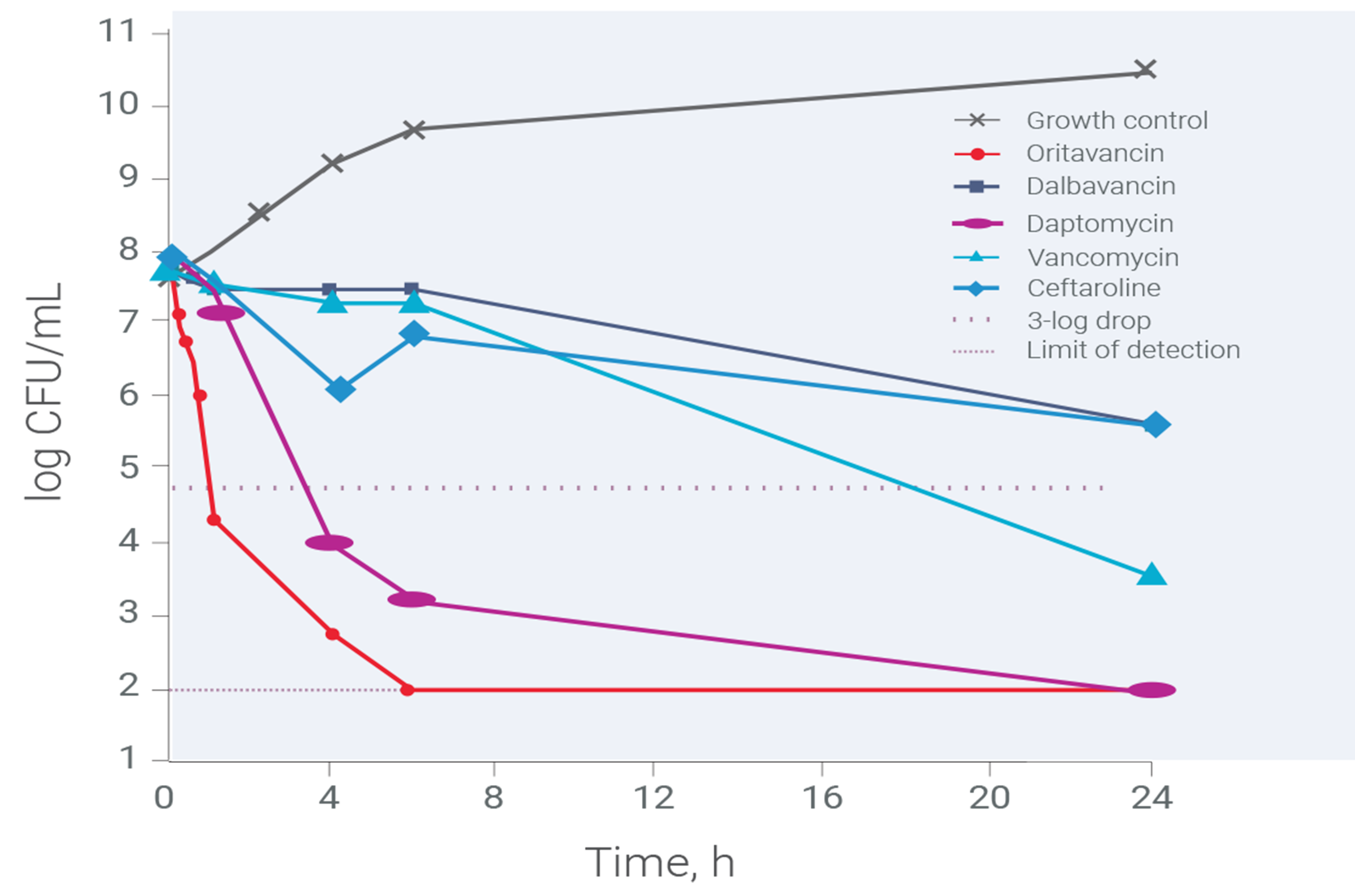
- At the high inoculum density, oritavancin was the only tested agent that demonstrated rapid bactericidal activity (0.25-1 hour) against both MSSA and MRSA, consistent with that observed against a standard inoculum density9
- – Oritavancin achieved the 3-log kill within 1 hour against MRSA NRS384 (USA 300) compared to daptomycin by 4 hours21
- – The activity of the other evaluated agents was largely bacteriostatic9
- Maintaining bactericidal activity at high inoculum density may be relevant in the context of staphylococcal infections where dense foci of pathogens may be present locally9
aORBACTIV® (oritivancin) has head-to-head clinical trial data versus vancomycin only. In vitro activity does not necessarily correlate to clinical efficacy.
‡ High inoculum density was approximately 7.5 x 107 CFU/mL.21
CFU, colony-forming units; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MSSA, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus.
Gram-positive bacteria, including MRSA, exhibit high in vitro susceptibility to KIMYRSA®†
ABSSSI, acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection; CFU, colony-forming units; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PK, pharmacokinetics.
References: 1. Data on file. Melinta Therapeutics. 2. Kimyrsa. Package insert. Melinta Therapeutics; 2021. 3. Zhanel GG, Calic D, Schweizer F, et al. New lipoglycopeptides: a comparative review of dalbavancin, oritavancin and telavancin [published correction appears in Drugs. 2011;71(5):526]. Drugs. 2010;70(7):859-886. doi:10.2165/11534440-000000000-00000 4. Orbactiv. Package insert. Melinta Therapeutics; 2019. 5. Arhin FF, Sarmiento I, Parr TR Jr, Moeck G. Activity of oritavancin and comparators in vitro against standard and high inocula of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;39(2):159-162. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.09.017 6. Arhin FF, Sarmiento I, Moeck G. Oritavancin retains bactericidal activity in vitro against standard and high inocula of heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (hVISA). Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013;41(4):397-398. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.12.004 7. Data on file. Melinta Therapeutics. 8. Staphylococcus aureus Belley A, Seguin DL, Arhin F, Moeck G. Comparative in vitro activities of oritavancin, dalbavancin, and vancomycin against methicillin-resistant isolates in a nondividing state. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(7):4342-4345. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00169-16 9. Sweeney D, Shinabarger DL, Arhin FF, Belley A, Moeck G, Pillar CM. Comparative in vitro activity of oritavancin and other agents against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017;87(2):121-128. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2016.11.002
*INDICATION AND USAGE
- Both KIMYRSA® and ORBACTIV® are oritavancin products that are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused or suspected to be caused by susceptible isolates of the following gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-susceptible [MSSA] and methicillin-resistant [MRSA] isolates), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus group (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), and Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only).
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of oritavancin and other antibacterial drugs, oritavancin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
- KIMYRSA® and ORBACTIV® are not approved for combination use and have differences in dose strength, duration of infusion, and preparation instructions, including reconstitution and dilution instructions and compatible diluents. Please see the full Prescribing Information for each product.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindications
- Use of intravenous unfractionated heparin sodium is contraindicated for 120 hours (5 days) after oritavancin administration because the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) test results may remain falsely elevated for approximately 120 hours (5 days) after oritavancin administration.
- Oritavancin products are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to oritavancin.
Warnings and Precautions
- Coagulation test interference: Oritavancin has been shown to artificially prolong aPTT for up to 120 hours, and may prolong PT and INR for up to 12 hours and ACT for up to 24 hours. Oritavancin has also been shown to elevate D-dimer concentrations up to 72 hours. For patients who require aPTT monitoring within 120 hours of oritavancin dosing, consider a non-phospholipid dependent coagulation test such as a Factor Xa (chromogenic) assay or an alternative anticoagulant not requiring aPTT.
- Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with the use of oritavancin products. Discontinue infusion if signs of acute hypersensitivity occur. Closely monitor patients with known hypersensitivity to glycopeptides.
- Infusion related reactions: Infusion reactions characterized by chest pain, back pain, chills and tremor have been observed with the use of oritavancin products, including after the administration of more than one dose of oritavancin during a single course of therapy. Stopping or slowing the infusion may result in cessation of these reactions.
- Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea: Evaluate patients if diarrhea occurs.
- Concomitant warfarin use: Oritavancin has been shown to artificially prolong PT/INR for up to 12 hours. Patients should be monitored for bleeding if concomitantly receiving oritavancin products and warfarin.
- Osteomyelitis: Institute appropriate alternate antibacterial therapy in patients with confirmed or suspected osteomyelitis.
- Prescribing oritavancin products in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions (≥3%) in patients treated with oritavancin products were headache, nausea, vomiting, limb and subcutaneous abscesses, and diarrhea. The adverse reactions occurring in ≥2 patients receiving KIMYRSA® were hypersensitivity, pruritus, chills and pyrexia.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for ORBACTIV®.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for KIMYRSA®.
Important Safety Information*INDICATION AND USAGE
Both KIMYRSA® and ORBACTIV® are oritavancin products that are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused or suspected to be
ContraindicationsUse of intravenous unfractionated heparin sodium is contraindicated for 120 hours (5 days) after oritavancin
- Real Patient Results
- SOLO Studies
- Mechanisms
- ABSSSI
- ABSSSI
This site is intended for US Healthcare Professionals only.


