- Treatment
Landscape- ABSSSI
Treatment
Burden- ABSSSI
Treatment
Challenges- About
KIMYRSA®- What is
KIMYRSA®?- Mechanisms
of Action- PK Profile
- In Vitro
Results by Pathogen- Clinical
Studies- Clinical Study Information
- SOLO Studies
- Real-World
Experience- Real-World Studies
- Real Patient Results
- Clinical Expert Videos
- Single-Dose
Administration- Resources
and Support- Patient Support Programs


Give them back their days with KIMYRSA®

KIMYRSA® is the first 1-hour oritavancin infusion product that can help alleviate the challenges of treating patients with ABSSSIs1
KIMYRSA simplifies and streamlines ABSSSI treatment for you and your patients:
- Administration in multiple care settings with no hospital stay required8
- Freedom from PICC lines9
- No dosing adjustments based on age, weight, or mild-to-moderate renal or hepatic impairment1
- The only long-acting lipoglycopeptide with 1-vial preparation1
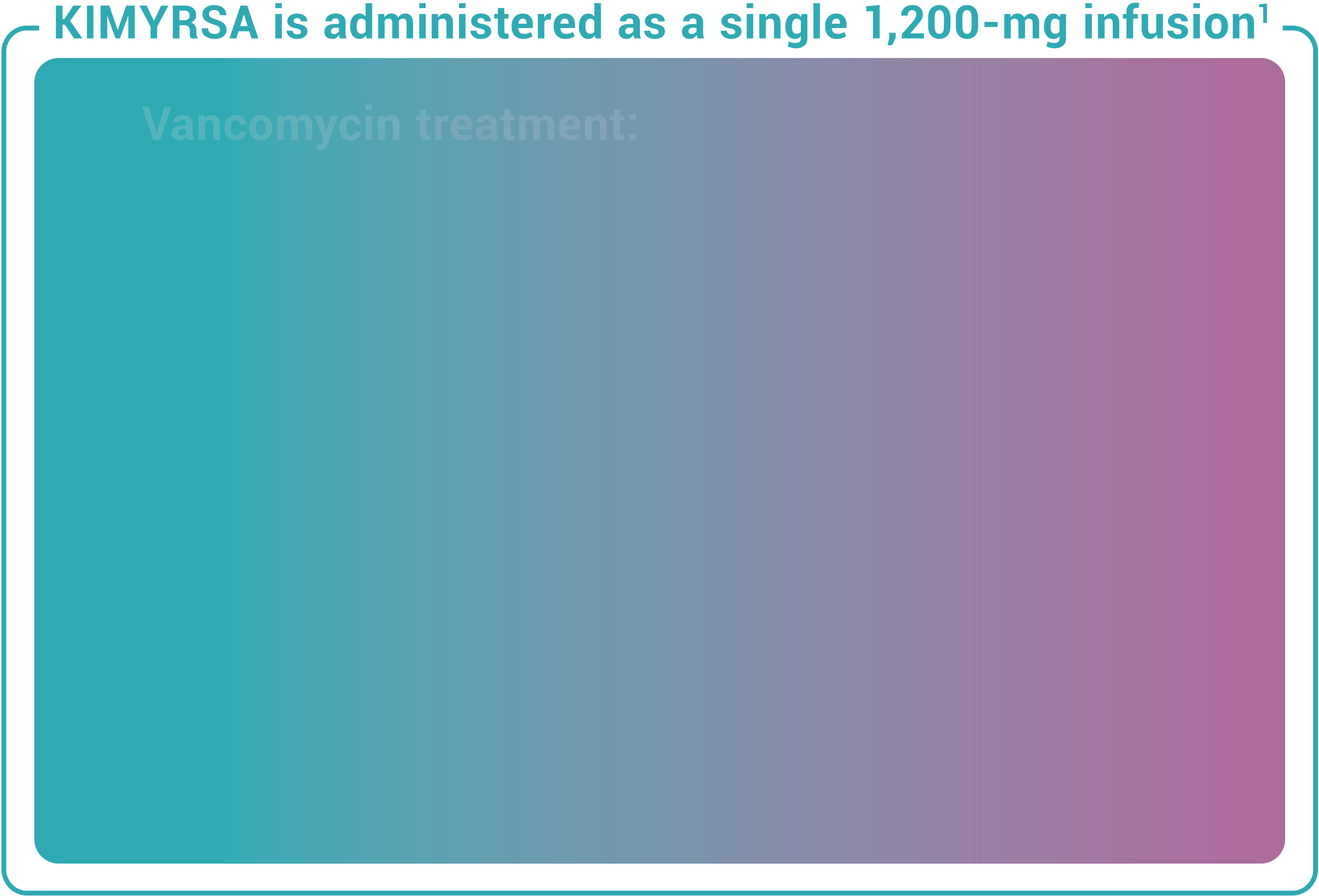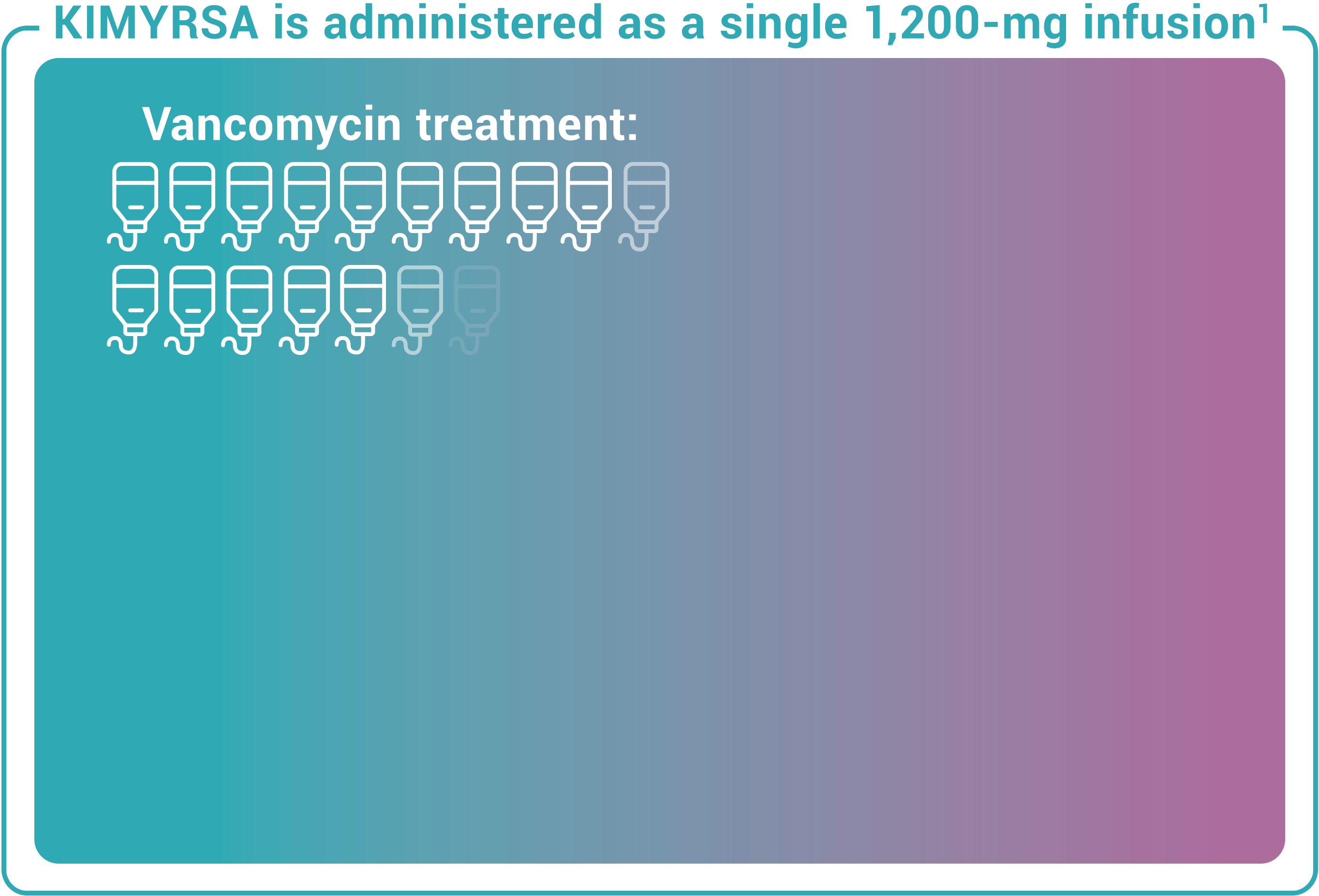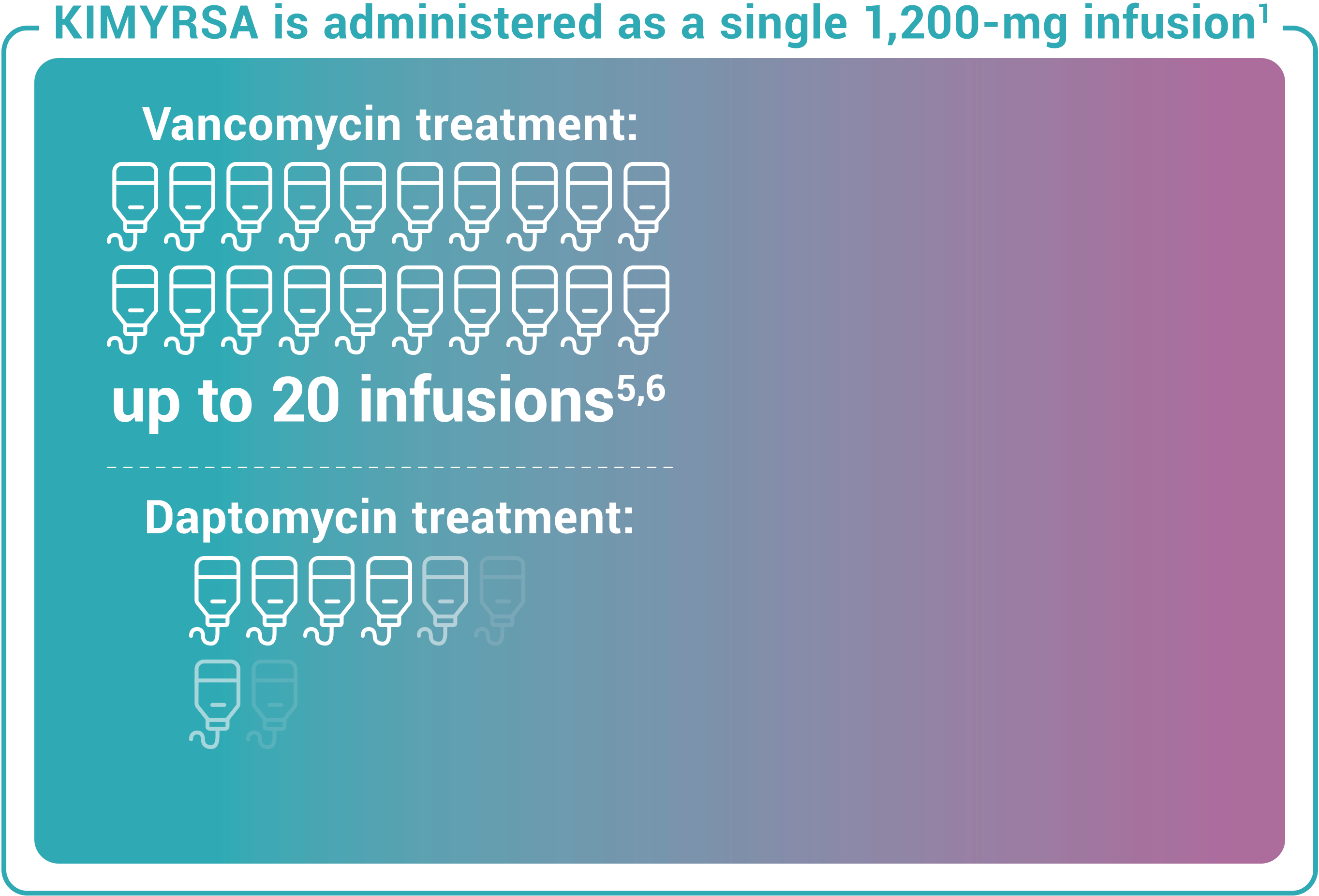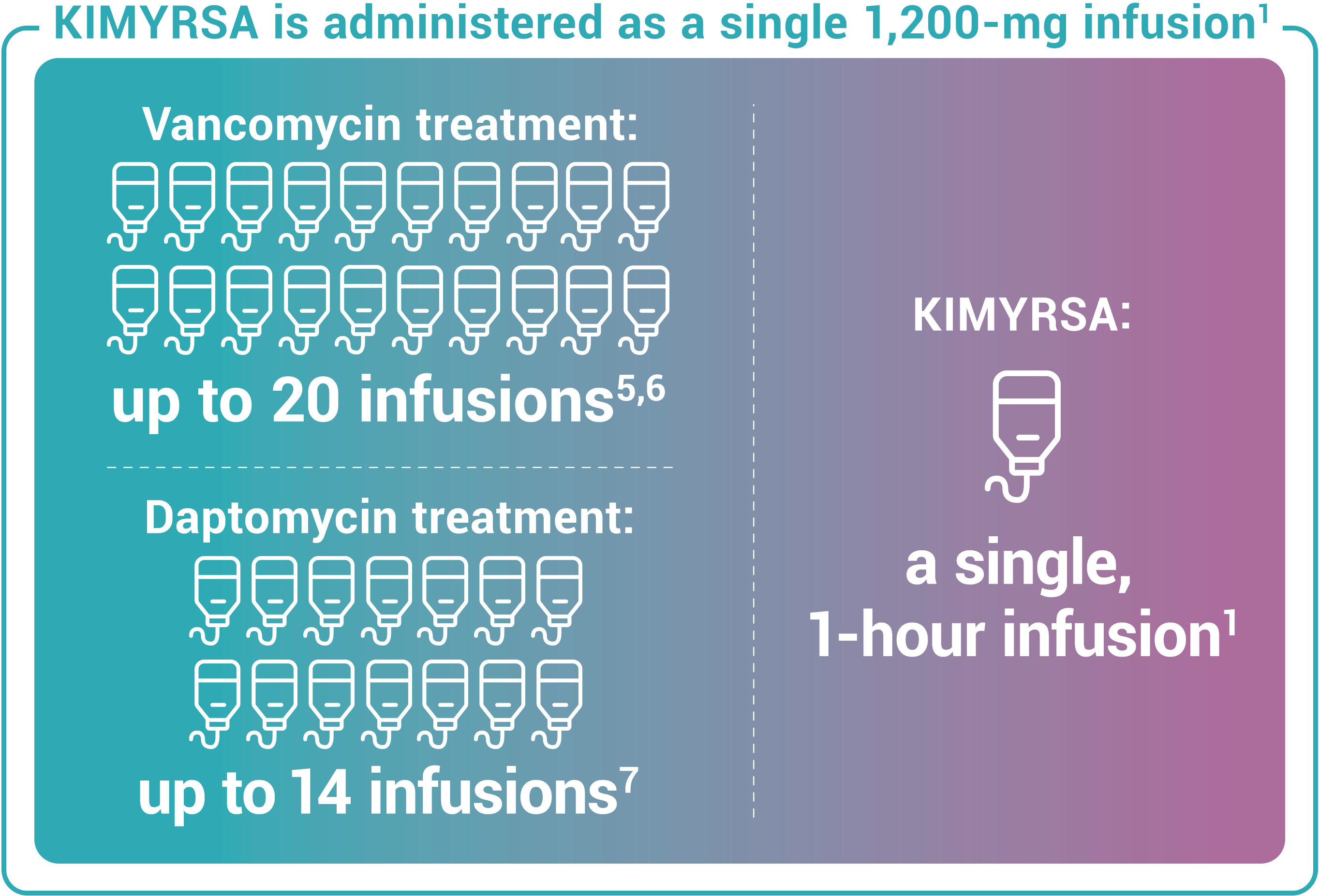
Recommended dosing for KIMYRSA® is a single 1,200-mg dose administered by intravenous infusion over 1 hour in patients 18 years and older. One KIMYRSA® 1,200-mg single-dose vial must be reconstituted in sterile water for injection (WFI) and then diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride injection or 5% dextrose in water (D5W) to prepare a single 1,200-mg intravenous dose.1
ABSSSI, acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection; PICC, peripherally inserted central catheter.
KIMYRSA® is the only 1-hour ABSSSI antibiotic with 3 mechanisms of action for a powerful bactericidal effect1a
aIn vitro data does not necessarily correlate to clinical efficacy.
References: 1. Kimyrsa. Package insert. Melinta Therapeutics; 2021. 2. Redell M, Moeck G, Lucasti C, et al. A real-world patient registry for oritavancin demonstrates efficacy and safety consistent with the phase 3 SOLO program. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018;5(6):ofy051. doi:10.1093/ ofid/ofy051 3. Whittaker C, Lodise TP, Nhan E, Reilly J. Expediting discharge in hospitalized, adult patients with skin and soft tissue infections who received empiric vancomycin therapy with oritavancin: description of findings from an institutional pathway. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2020;7(suppl 1):30-35. doi:10.1007/s40801-020-00196-6 4. Williams B, Muklewicz J, Steuber T, Williams A, Edwards J. Comparison of inpatient standard-of-care to outpatient oritavancin therapy for patients with acute uncomplicated cellulitis. J Pharm Pract. 2023;36(1):27-32. doi:10.1177/08971900211021258 5. Corey G, Arhin F, Wikler MA, et al. Pooled analysis of singledose oritavancin in the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections caused by gram-positive pathogens, including a large patient subset with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;48(5):528-534. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.07.019 6. Vancomycin. Package Insert. ANI Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2022. 7. Daptomycin. Package insert. Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC; 2022. 8. Lodise T, Redell M, Armstrong S, Sulham K, Corey G. Efficacy and safety of oritavancin relative to vancomycin for patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) in the outpatient setting: results from the SOLO clinical trials. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4(1):ofw274. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofw274 9. Dretske D, Schulz L, Werner E, Sharp B, Pulia M. Effectiveness of oritavancin for management of skin and soft tissue infections in the emergency department: a case series. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;43:77-80. doi: 10.1016/j. ajem.2021.01.050
*INDICATION AND USAGE
- Both KIMYRSA® and ORBACTIV® are oritavancin products that are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused or suspected to be caused by susceptible isolates of the following gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-susceptible [MSSA] and methicillin-resistant [MRSA] isolates), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus group (includes S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus), and Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only).
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of oritavancin and other antibacterial drugs, oritavancin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
- KIMYRSA® and ORBACTIV® are not approved for combination use and have differences in dose strength, duration of infusion, and preparation instructions, including reconstitution and dilution instructions and compatible diluents. Please see the full Prescribing Information for each product.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindications
- Use of intravenous unfractionated heparin sodium is contraindicated for 120 hours (5 days) after oritavancin administration because the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) test results may remain falsely elevated for approximately 120 hours (5 days) after oritavancin administration.
- Oritavancin products are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to oritavancin.
Warnings and Precautions
- Coagulation test interference: Oritavancin has been shown to artificially prolong aPTT for up to 120 hours, and may prolong PT and INR for up to 12 hours and ACT for up to 24 hours. Oritavancin has also been shown to elevate D-dimer concentrations up to 72 hours. For patients who require aPTT monitoring within 120 hours of oritavancin dosing, consider a non-phospholipid dependent coagulation test such as a Factor Xa (chromogenic) assay or an alternative anticoagulant not requiring aPTT.
- Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with the use of oritavancin products. Discontinue infusion if signs of acute hypersensitivity occur. Closely monitor patients with known hypersensitivity to glycopeptides.
- Infusion related reactions: Infusion reactions characterized by chest pain, back pain, chills and tremor have been observed with the use of oritavancin products, including after the administration of more than one dose of oritavancin during a single course of therapy. Stopping or slowing the infusion may result in cessation of these reactions.
- Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea: Evaluate patients if diarrhea occurs.
- Concomitant warfarin use: Oritavancin has been shown to artificially prolong PT/INR for up to 12 hours. Patients should be monitored for bleeding if concomitantly receiving oritavancin products and warfarin.
- Osteomyelitis: Institute appropriate alternate antibacterial therapy in patients with confirmed or suspected osteomyelitis.
- Prescribing oritavancin products in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions (≥3%) in patients treated with oritavancin products were headache, nausea, vomiting, limb and subcutaneous abscesses, and diarrhea. The adverse reactions occurring in ≥2 patients receiving KIMYRSA® were hypersensitivity, pruritus, chills and pyrexia.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for ORBACTIV®.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for KIMYRSA®.
Important Safety Information*INDICATION AND USAGE
Both KIMYRSA® and ORBACTIV® are oritavancin products that are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused or suspected to be
ContraindicationsUse of intravenous unfractionated heparin sodium is contraindicated for 120 hours (5 days) after oritavancin
- Real Patient Results
- SOLO Studies
- Mechanisms
- ABSSSI
- ABSSSI
This site is intended for US Healthcare Professionals only.


